Discover how Salesforce integration tools like MuleSoft, Salesforce Connect, Heroku Connect, and APIs streamline data synchronization, automate workflows, and enhance efficiency. Learn their purposes, real-world applications, and how they empower businesses to create unified digital ecosystems.
Salesforce is a powerful CRM platform, but its true potential is unlocked when integrated with other systems. Integration ensures that Salesforce communicates seamlessly with ERP systems, databases, APIs, and other applications. This tutorial explains the key integration tools, their purpose, and real-world applications using the table below as a guide.
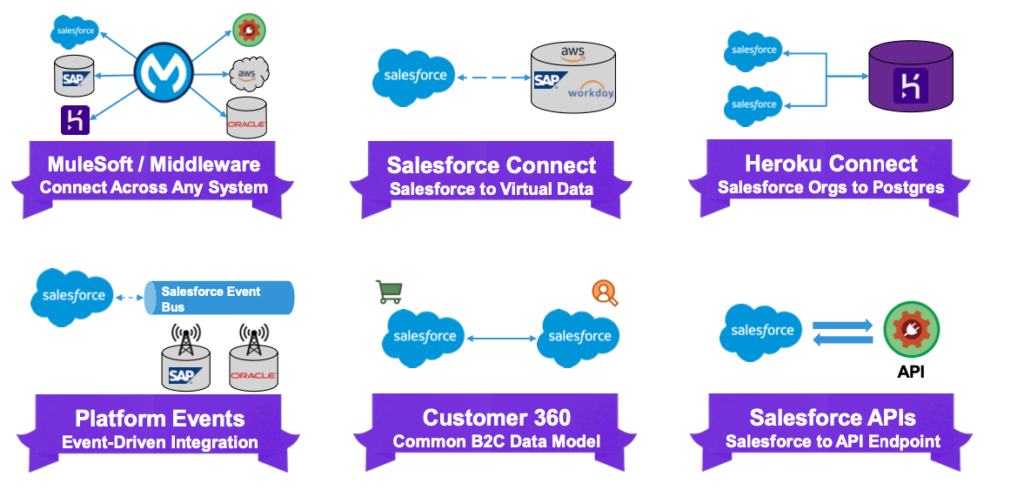
| Integration Tool | Purpose | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| MuleSoft / Middleware | Connect Salesforce with multiple external systems like SAP, AWS. | Centralized platform for integrating Salesforce with ERP systems (e.g., real-time data sync). |
| Salesforce Connect | Access external virtual data in real-time without storing it. | Fetch live data from SAP HANA or Workday for reporting without replicating it in Salesforce. |
| Heroku Connect | Sync Salesforce data with Heroku Postgres databases. | Real-time integration for apps built on Heroku, such as syncing orders or campaign data. |
| Platform Events | Enable real-time, event-driven integrations between systems. | Update external systems (e.g., SAP or Oracle) instantly when changes occur in Salesforce. |
| Customer 360 | Provide a unified data model for customer interactions. | Deliver personalized customer experiences by consolidating data from multiple sources. |
| Salesforce APIs | Connect Salesforce to external systems using APIs (REST, SOAP). | Integrate with payment gateways or inventory systems for seamless data exchanges. |
Understanding Salesforce Integration Tools
1. MuleSoft / Middleware
- Purpose: MuleSoft acts as middleware, enabling Salesforce to connect with a wide range of systems, such as SAP, Oracle, AWS, and others.
- How It Works: MuleSoft creates APIs and data pipelines that facilitate real-time or scheduled data exchange between Salesforce and external platforms.
- Example: A company integrates Salesforce with its ERP system (SAP) to synchronize inventory data. Sales reps in Salesforce can now check live inventory availability during order creation.
2. Salesforce Connect
- Purpose: Allows Salesforce to access external data sources in real-time without replicating data into Salesforce.
- How It Works: Using OData protocols, Salesforce queries and displays virtual data from systems like Workday or SAP HANA.
- Example: A retail company needs to access inventory levels stored in SAP HANA for its Salesforce dashboards. Instead of duplicating data, Salesforce Connect fetches live inventory data when required.
3. Heroku Connect
- Purpose: Synchronizes Salesforce data with Heroku Postgres databases.
- How It Works: Heroku Connect establishes a real-time link between Salesforce objects and Heroku’s Postgres database, keeping both systems in sync.
- Example: A business using Heroku for its e-commerce app integrates Heroku with Salesforce to sync order details, ensuring customers’ purchase history is available in Salesforce.
4. Platform Events
- Purpose: Enables event-driven integration by publishing and subscribing to events between systems.
- How It Works: Salesforce sends notifications (events) when specific actions occur, such as updates to an order. External systems subscribe to these events to stay updated in real time.
- Example: When an order status changes in Salesforce, a Platform Event triggers SAP to update its production schedule instantly.
5. Customer 360
- Purpose: Provides a unified view of customer interactions by consolidating data from multiple systems.
- How It Works: Salesforce Customer 360 uses a common B2C data model to integrate data from Salesforce and external platforms like marketing tools or e-commerce systems.
- Example: A company integrates Salesforce with its marketing automation tool to track customer interactions across platforms, enabling personalized campaigns.
6. Salesforce APIs
- Purpose: Connects Salesforce to other systems using REST or SOAP APIs for data exchange.
- How It Works: External systems call Salesforce APIs to create, update, or retrieve records and vice versa.
- Example: A payment gateway calls Salesforce APIs to update payment statuses, ensuring sales reps see real-time transaction updates.
Benefits of Salesforce Integration
- Real-Time Data Synchronization: Integration tools ensure that data is always up-to-date, improving operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Productivity: Automating workflows across systems eliminates manual errors and repetitive tasks.
- Improved Customer Experience: Integration enables businesses to deliver personalized services by leveraging unified customer data.
- Scalability: These tools allow businesses to expand integrations as their needs grow.
Conclusion
Salesforce’s integration tools empower businesses to create a unified digital ecosystem. From middleware solutions like MuleSoft to real-time data access with Salesforce Connect and event-driven updates via Platform Events, these tools cater to diverse integration needs. By leveraging these solutions, businesses can enhance productivity, deliver better customer experiences, and streamline operations.
Start using these tools to unlock the full potential of Salesforce and elevate your business processes!