Welcome to our Salesforce and SAP Integration Tutorial. Here, we explore how to connect Salesforce’s CRM with SAP’s ERP for a seamless flow of data, enabling unified customer and operational insights. This integration streamlines workflows and enhances business efficiency.
Salesforce and SAP integration offers a powerful way to unify front-office and back-office operations, providing a single source of truth for sales, service, and operational teams. This tutorial will guide you step-by-step, covering the integration process, key methods, and best practices to get started efficiently.
Introduction to Salesforce and SAP Integration
Salesforce is a leading CRM system that manages customer relationships, while SAP is an ERP system known for handling backend functions like finance, supply chain, and logistics. By integrating these platforms, businesses can unify front-office and back-office processes, enhance customer satisfaction, and achieve a seamless flow of data.
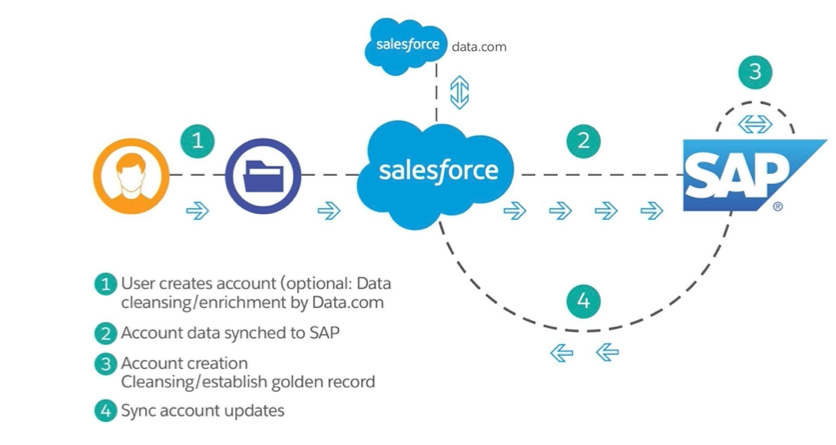
Key Benefits of Salesforce and SAP Integration
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Unified Data Flow | Eliminates silos by synchronizing customer and operational data across systems. |
| Improved Efficiency | Reduces the need for manual data entry, minimizing errors and saving time. |
| Enhanced Customer Insights | Offers a comprehensive view of customers by combining sales, support, and financial data. |
| Streamlined Processes | Automates workflows from lead generation to order fulfillment, improving overall process efficiency. |
| Scalability | Enables the business to grow seamlessly, adapting to new challenges without infrastructure issues. |
Core Integration Approaches
Understanding the right approach to integrating Salesforce and SAP is critical for a successful outcome. Below, we’ll discuss four main approaches, each suitable for different scenarios and business needs.
Integration Options Explained
| Integration Approach | Description | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Point-to-Point | Directly connects Salesforce and SAP via APIs. Simple to implement but can become cumbersome as complexity grows. | Small-scale projects with straightforward requirements. |
| Middleware Solutions | Middleware (e.g., MuleSoft, SAP CPI) handles communication between Salesforce and SAP. This provides scalability, flexibility, and robust security. | Large-scale, complex projects needing seamless integration. |
| Batch Data Sync | Data is periodically synchronized (e.g., nightly updates). Ideal for non-time-critical data like product catalogs or pricing updates. | Synchronizing non-urgent data. |
| Real-Time Integration | Uses APIs for instant data synchronization between systems. Suitable for business-critical processes that require real-time data, like order processing. | Critical workflows that need instant updates. |
1. Point-to-Point Integration
This approach uses APIs to create direct connections between Salesforce and SAP. It is quick to implement and works well for simple use cases, such as when there is a need to update customer information in both systems. However, it lacks scalability and can quickly become complex with multiple integration points.
2. Middleware-Based Integration
Middleware platforms such as MuleSoft or SAP PI/PO act as a bridge between Salesforce and SAP, allowing for smoother communication between systems. Middleware simplifies the integration, especially for businesses needing to connect multiple systems beyond just Salesforce and SAP. Middleware also offers scalability, security, and monitoring capabilities, which are critical for managing complex integrations.
3. Batch Data Synchronization
In some cases, real-time data integration isn’t needed. Batch data synchronization works well when data can be updated periodically, for instance, by syncing inventory levels every night. This method is suitable for processes where immediate data updates aren’t necessary, helping save costs and reduce processing loads.
4. Real-Time Integration
Real-time integration uses APIs to instantly synchronize data between Salesforce and SAP. It is essential for business processes like order creation, where every change needs to be reflected immediately in both systems. Real-time integration enables your sales and customer service teams to provide accurate and up-to-date information at all times.
Common Use Cases for Salesforce and SAP Integration
Salesforce and SAP integration addresses many common business scenarios. Let’s explore a few:
| Use Case | Details |
|---|---|
| Customer Account Management | Integrates customer account data to ensure Salesforce and SAP have consistent and up-to-date records. |
| Product Pricing & Quoting | Sales reps can generate quotes in Salesforce using pricing information from SAP, ensuring accuracy and consistency across platforms. |
| Opportunity-to-Order Process | When an opportunity closes in Salesforce, the order details are sent to SAP for execution, reducing manual steps and ensuring accurate order handling. |
| Financial Data Integration | Displays financial information such as invoices and payment status from SAP directly within Salesforce, providing easy access for customer-facing teams. |
Customer Account Management
Customer account management is one of the most vital aspects of integration. By syncing accounts in Salesforce and SAP, you ensure that sales, support, and finance teams work with the same customer data, minimizing errors and improving communication. This bi-directional synchronization keeps both systems up-to-date and ensures data consistency.
Product Pricing and Quoting
Integrating SAP’s pricing engine with Salesforce is a game-changer for sales reps. Imagine being able to generate accurate quotes without switching platforms. This integration not only saves time but also ensures pricing accuracy, which is critical when dealing with large or complex product portfolios.
Opportunity-to-Order Workflow
The opportunity-to-order workflow is a typical use case where Salesforce and SAP integration shines. Sales reps track opportunities in Salesforce. Once a deal is won, the order details are sent directly to SAP for fulfillment. This smooth handover reduces manual input and ensures faster delivery, which is crucial for customer satisfaction.
Financial Data Integration
Financial data such as invoices, payment status, and order history are essential for managing customer relationships effectively. By making this information available in Salesforce, account managers can quickly address customer queries related to billing or payments, all without switching systems.
Key Considerations for a Successful Integration
Integration can be complex, but with proper planning and execution, you can overcome the common challenges. Here are some key considerations:
| Key Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
| Define Requirements | Identify what data entities need synchronization (e.g., orders, accounts) and what tasks (e.g., updates, deletions) will be performed. |
| Evaluate Enterprise Architecture | Choose an integration approach that aligns with your existing architecture—cloud, on-premises, or hybrid. |
| Select Key Integration Tools | Choose tools like APIs or middleware that best suit your business needs. |
| Set Clear KPIs | Track performance metrics such as synchronization latency and data accuracy to ensure integration success. |
Conclusion
Salesforce and SAP integration brings a wealth of benefits to organizations looking to unify their business operations. From ensuring accurate customer account management to enabling real-time financial data visualization, this integration can significantly enhance efficiency, streamline workflows, and improve customer satisfaction.
Choosing the right integration approach—whether it’s point-to-point, middleware-based, batch sync, or real-time—depends on your business needs. Consider your current infrastructure, growth plans, and operational needs to select the most suitable solution. By focusing on data accuracy, using scalable tools, and following best practices, businesses can ensure a successful integration that empowers every department.
Embrace the power of Salesforce and SAP integration to keep your teams aligned, your customers happy, and your operations running seamlessly.